Mind&VR UC-win/Road for MindSet
 |
|
Linkage of Mindset Unit which measures the brain activity with VR
Background
In the old days, the only way for a human to input any information to a computer was through the use of keyboard, a mouse, a joystick, or a 3D mouse. Now the input method via hand gesturing as in games is becoming more common. Nintendo's Wii, PlayStation Move, Microsoft Kinect, etc. allow the interaction between a human and the gaming system without the use of any special device. In order to perform a high level task such as controlling vehicles or robots before the background that portrays the world of ever changing technology, FORUM8 is developing an EEG based device.
Investigation on Handless Control
The first device we used to integrate handless control is the MindSet from
NeuroSky. It is basically a Bluetooth headset with the ability to measure
the brain activity (EEG). It has two headphones and one microphone (Figure
1). Three electrodes on the left ear headphone and one electrode on the
user's forehead allows the device to record the raw EEG signal characterizing
the brain activity of the user. From the analysis of the raw EEG signal,
the components of the signal can be extracted (Alpha wave, Beta wave, Gamma
wave, Delta Wave, Theta wave), as well as two parameters, the Meditation
factor and the Attention factor (Figure 2). Each of these factors characterize
the state of mind of the user. The mediation factor increases when the
user relaxes while the Attention factor increases when the user focuses
his mind on a specific thought.
 |
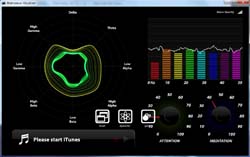 |
Figure 1 MindSet Unit
(Neurosky) |
Figure 2 "Brainwave Vizualizer"
(Neurosky) |
Application : F1 race
Our first application using EEG based technology is a Formula 1 race. We
developed an interface that allows to read two MindSet units, in real time
(@60Hz) (Figure 3), with extraction of the Meditation and Attention factors.
 |
Figure 3
Import and extraction of the Meditation and Attention factors
of 2 MindSet units (Gradation of red and green) |
The F1 race takes place on the Phoenix street circuit in Arizona, US (Figure
4). The interface was implemented as a server so the two players can race
on separate machines. The acceleration of the car is controlled by the
Attention parameter, the more the user can focus his thoughts, the faster
the car is moving. FORUM8 proposes the research system using biological
information of brain wave.
 |
|
 |
| Figure 4 Phoenix F1 Circuit |
|
Figure 5 Popular as the exhibition system for its game element |
|
|
Kinect Driving Simulator
 |
|
Handless driving simulation with infrared sensor
This system allows you to operate driving within UC-win/Road by the movement
of both hands like operating the steering wheel in front of the Kinect.
The position information of the both hands of a driver detected by the
Kinect is converted to steering wheen, acceleration and brake of a car.
What is Kinect Sensor?
Kinect Sensor (Hereinafter, Kinect) is used as a peripheral device of "Xbox360®"which is a home-use game machine sold by Microsoft and is the device which allows you to operate the system via physical behavior, gesture and voice without a controller. A camera and sensor are mounted on it and players are automatically recognized when they stand in front of the Kinect.
This technology is based on the depth camera technology developed by PrimeSense. The sensor includes a VGA camera, 3D scanner, 4 microphones, inclined motor, etc. The 3D scanner is composed of an infrared laser (whose frequency is a little lower than that of a red signal) that gives off several dots in a continuous pattern. Although the laser is not visible to the naked eye (as the wave length is about 780nm), it can be detected by an infrared camera(Figure 1a and 1b).
 |
|
 |
Figure 1a
A night-vision image of Kinect |
|
Figure 1b
Expanded view with points
projected on the wall |
The distance from the sensor to the point is predicted via infrared depth
camera and the depth map of ambient environment is created.
| Figure 2 Depth map of the ambient environment given in the camera feed |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| Figure 2a VGA camera output |
|
Figure 2b Depth map of the ambient environment |
|
Figure 2c Camera output and depth map (composite view) |
The Kinect has the following features.
- Motion capture (up to 6) and gesture recognition. The interface can be controlled by the gesture.
- Recognition of the facial expression. It can recognize the user to automatically switch the setting.
- Voice recognition. The voice command can be executed.
- Wheel base. Its inclination angle of the center can be adjusted according
to the optimal tracking.
Vehicle control and imaging of driving operation via Kinect
Linkage with UC-win/Road enables you to experience the driving simulation by holding the virtual steering wheel and moving the arms. It is possible to keep the natural situation which is very close to the actual driving operation.
- Steering operation (Right-turning, Left-turning)
The steering can be operated same as actual steering control. It supports
for both of right-turning and left-turning.
- Acceleration operation
It can be accelerated by moving the arms from the neutral position to the front. The further you move the arms, the larger the acceleration amount becomes.
- Braking operation
The braking operation is performed by moving the arms from the neutral
position to the back. The further you move the arms, the larger the braking
amount becomes.
- Detection of steering angle and steering direction
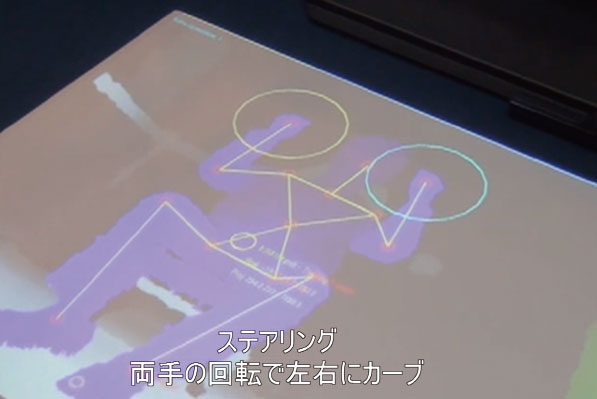
The right and left direction of the steering wheel and its steering angle
are detected as an analog value from the positional relationship betweeen
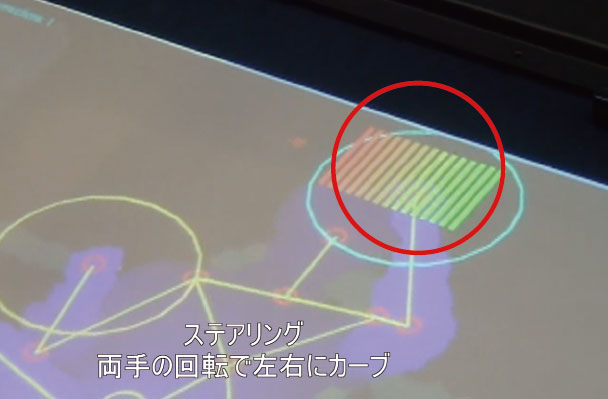
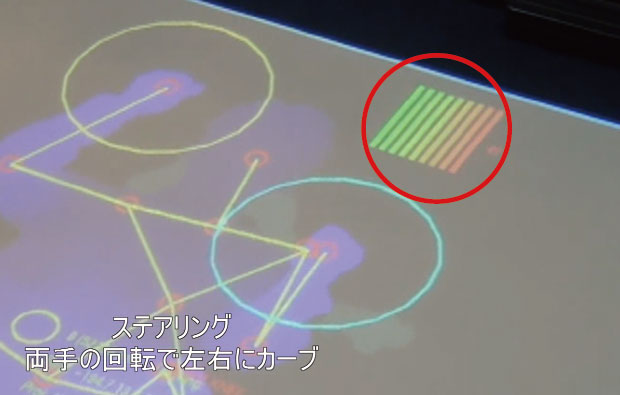
the user's right and left fist. How much the steering wheel is turned is
indicated by a row of bars that change color from green to red. The bigger
the steering angle, the more red the bar will be.
 |
 |
 |
| Travel in a straight line |
Right turn : As you steer to the right, the red bars will increase in the
right direction. |
Left turn : As you steer to the left, the red bars will increase in the
left direction. |
- Distingishing accelerator from brake
Acceleration and braking can be distinguished by detecting the angles between
the right toe opening right and left.
 |
 |
| Accelerator position |
Braking position |
- Distingishing accelerator from brake
Accelerator
This is detected as an analog value from the amount of pressure the driver exerts on the accelerator pedal. In case of accelerator, the stack of bars will increase in the upward direction.
Brake
This is detected as an analog value from the amount of pressure the driver exerts on the brake pedal. In case of brake, the stack of bars will increase in the downward direction.
|
|
