|
 |
| From Website of Toi Lab. |
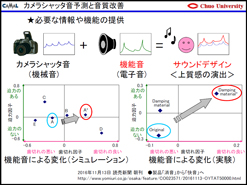
Idea for Sound Quality
Improvement and Concept of
Comfortable Sound Design
"In old days, noises were so loud. Today, noises have become much smaller than the old days even in the offi ce environment."
It can be said that this is the result of working hard for noise reduction.
On the contrary, however, "small noises" are now becoming obvious.
Is it good to decrease the sound volume until no sound is heard? If so,
no audible information can be obtained, even producing weird feeling. Then
he wondered if the idea of sound quality improvement was needed. This was
the motivation for him to start studying the concerned area, says Prof.
Toi.
"In the beginning, we were designing comfortable sound for each product".
Then it was converted to the idea like "let's make suitable sound
depending on what is necessary in living environment or according to the
time zones or purposes." Prof. Toi had come to pursue the stance to
assume each of the sound source being a musical instrument and coordinate
them so that people living there would not get tired or can feel them as
comfortable acoustic environment (smart sound design).
In other words, the traditional approach was to manufacture something,
and if the produced sound was bad, it would be regarded as uncomfortable
sound and processed for noise reduction. On the contrary, he positioned
production of sound to improve comfortability as "comfortable sound
design". At the fi rst stage of manufacturing automobiles or household
appliance, sound is determined to defi ne whether or not this contributes
to the functionality of the product itself, for example, asking "is
this comfortable to use if we make the sound like this?" To do so,
however, it is necessary to evaluate the present sound. After that, the
setting goal of sound should be decided. Then, a method has been formed
to consider the whole thing throughout the process from evaluation to the
feedback of design, for example, "How will the sound be changed by
changing where in what way?", or "How should the design be changed
to produce this sound?".
|
 |
 |
| Research cases on acoustics in the Lab |
Utilizing Diverse ICT, Unique
Research Developed in Broad Areas
When he established the lab 20 years and more ago, the term "comfortable
sound" itself was hardly used. Therefore, he needed to explain from
its defi nition even when he was making presentation in academic meetings.
In recent years, however, the concept of "sound quality improvement"
and "comfortable sound design" have penetrated so widely that
they are ordinarily used.
On the other hand, "Acoustic Systems Laboratory" has about 10
undergraduate students and another 10 or so graduate students, and several
researchers dedicated for joint research on the register. Regarding joint
research with companies that the lab started to take in positively early,
more than 10 themes are progressing at the same time in a year. Each theme
is positioned as a project for 2 to 3 years. So far 200 and some 10 themes
have been dealt in total.
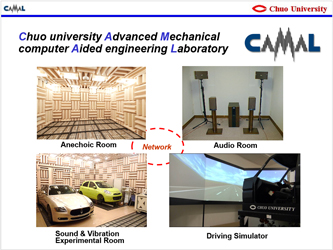
| One of the important facilities for these researches is an anechoic room.
The Lab uses multiple rooms according to the purpose. They include two
anechoic rooms as well as a semianechoic room capable of accommodating
actual vehicles and large structures, which is the largest scale for a
university in Tokyo. The Lab also utilizes wide-ranging ICT (information
and communication technology). For example, they use software for oscillation
analysis, acoustic analysis, and different kinds of numerical simulation;
sensors to measure bio-information, acceleration, and sound pressure; measuring
equipment to measure oscillation or acoustics, and various kinds of simulators.
|
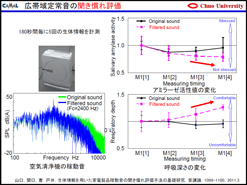
| Especially, combining and merging multiple software programs in their own way, the Lab is trying to draw evaluations from such points of view that have been overlooked so far, or feedback to the design based on these evaluations. "In fact, there are not so many elements to deal with sound in the
mechanical system."
Speaking of the world of sound, what are
generally known includes architectural acoustics
as well as electro-acoustics for deleting or
making sound (active noise control and
active sound control etc.). Based on precision
mechanics, the Lab started with a study on
noise that occurs from machines, refl ecting its
specialty. In expanding its objects steadily, the
Lab has been covering issues of sound in the
areas of vehicles, offi ces, living spaces, and
medical care and welfare.
|
|
 |
| Explaining sound design for living environment |
|
Introducing UC-win/Road for Studies
on Vehicles, Future Development and
Challenges of Studies
In recent years, Acoustic Systems Laboratory had tendency to do various
kinds of research on sound regarding automobiles using DS through joint
research etc. Prof. Toi reveals that his fi rst frank impression about
UC-win/Road was "being capable of creating motion pictures nicely,
with comparatively affordable price compared with other software programs
we have".
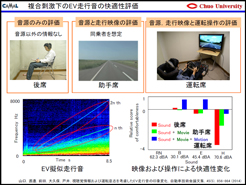
Several years ago, he came up with a research idea as follows: "Is
it alright that the driver's seat, the passenger seat, and back seats have
the same sound environment, or is it necessary to have different sound
environments for each seat?" In trying to build up experimental environment
for evaluating sound for each of "sound only", "sound and
vision", and "sound, vision, and driving operation" in the
laboratory, it is rather hard to handle without using a tool like UC-win/Road
in the part related to vision and driving operation. In particular, when
trying to add some driving conditions, the display and sound were required
to change linked with the acceleration and deceleration of the vehicle.
This made them consider introduction of UCwin/ Road to meet such needs.
Almost at the same time, as mentioned at the beginning, when he heard from
the working group studying acoustic evaluation in vehicle driving using
bio-information that they want to represent actual driving conditions more
realistically, in Sound quality evaluation technical committee (Society
of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.), with which he had been involved
from its establishment, he introduced UC-win/ Road to them, which was adopted
as a result.

|
 |
 |
Experimental environment for evaluating appropriate alarm sound created
with UC-win/Road
(simulation executed by switching day and night, clear and rainy sky) |
For example, for the scene where a person is running out of a side street,
UC-win/Road is actually used to create environment to see at what timing
the alarm sound should be made in advance for the driver to perceive the
scene more safely. He says that he realized its convenience in that it
is easy to switch day and night or clear and rainy weather. What's more,
it was made easier to represent the travelling environment, which was rather
diffi cult before. Additionally, since the created sham driving environment
changes according to acceleration (rapid and slow) or based on the driving
operation etc. for various kinds of events set on the route, it exerts
excellent oneness. Furthermore, he evaluates that it can be a very strong
tool since all logs are kept. Particularly, in the sense of seeing the
change in sound environment accompanied by operational system, UC-win/Road
is easy to use, and useful for constructing comfortable and functional
smart sound design, says Prof. Toi.
On the other hand, he expects from an acoustic specialist's point of view
that it makes it possible to raise the degree of freedom for sound such
as sound quality control. At the present, one of the big challenges is
to monitor human information. For example, if emotion can be monitored,
appropriate sound environment and oscillation environment are to be created
based on this. He says that what they should do from now in relation with
automobiles is to build up environments that refl ect fi ve senses based
on such monitoring.
 |
| Lab members around DS applying the experimental environment of UC-win/Road in the anechoic room |
|

